
高级宏观经济学学习笔记英文
60页1、Macroeconomics Lecture NotesTOPICS 2. The Solow Growth model 2-5 2. The Ramsey Growth model 6-11 3. Real BusinessCycle Theory 12-20 4. Traditional Keynesian Theories of Fluctuations 21-23 5. Microeconomic Foundations of Incomplete Nominal Adjustments 24- 39 6. Consumption 40-44 7. Investment 45-508. Inflation and Monetary policy 51-901Growth1.1The Solow Growth ModelAt any point in time, the economy has some amount of labor (L), capital (K) and knowledge (A) to produce output (Y). The production
2、function can be written asY (t) = F(K(t),A(t)L(t),(1)where t denotes time. The production function is assumed to have constantreturns to scale in capital and effective labor, (F(ck,cAL) = cF(K,AL) where c 0). Hence, we can write1 ALF(K,AL) = F?K AL,1? .(2)Defining k = K/AL, y = Y/AL and f(k) = F(K,1), we can rewrite equation (2) as:y = F(k)(3)Here, the output per effective labor depends on the capital per effective labor. The ”intensive” or ”per capita” form of the production function f(k)satisf
3、ies f(0) = 0,f0(k) 0,f00(k) 0 and k is rising. If k kthen (k) 0, n (1 )g 0(12)Note that determines the households willingness to shift consumption be-tween two periods (1/ can be defined as the elasticity of intertemporal sub- stitution between consumption at any two points in time.) As goes to 0, marginal utility falls more slowly as consumption rises so that the household is more willing to allow consumption to vary overtime. The last assumption, n (1 )g 0, ensures that lifetime utility does n
4、ot diverge.2.1.1The behavior households and firmsHouseholds budget constraint: The representative household take r and w as given. Since the household has L/H members, its labor income at t is W(t)L(t)/H and consumption expenditures are C(t)L(t)/H. Since interest rates over time can change, we write R(t) as (=Rt =0r()d). One unit of good invested at t = 0 yields eR(t)units of the good at time t (showing the effects of continuous compounding). The households consumption is C(t)L(t)/H and its init
《高级宏观经济学学习笔记英文》由会员实***分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《高级宏观经济学学习笔记英文》请在金锄头文库上搜索。

关于工会改革的几点思考考察心得

小学语文1~6年级阅读理解答题技巧北师大名师总结 新版

冀教版小学数学五年级上册同步练习新版

冀教版小学数学五年级上册教材习题参考答案新版

统编版三年级语文上册期末分类复习 基础+提高 适用于巩固提高

全网最全最新版链工宝2022年全国安全生产月知识竞赛题库及答案
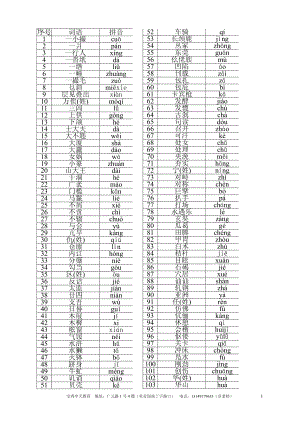
高考总复习 高考语文易错字音1000例
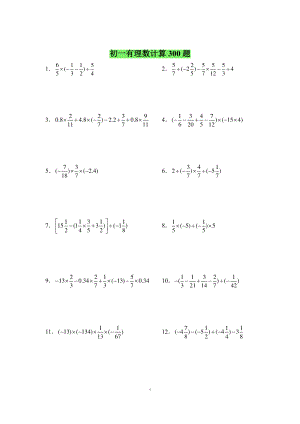
初中一年级书计算精选300题

普通话等级考试朗读范文含注音普通话考试朗读作品60篇 内含拼音与文字(1)

对国企领域违纪违法典型案例的剖析

冀教版小学数学五年级上册同步练习

冀教版小学数学四年级上册同步练习

冀教版小学数学六年级上册教材习题参考答案新版

冀教版小学数学四年级上册教材习题参考答案新版

冀教版小学数学四年级上册同步练习新版

部编教材1-6年级语文必背古诗文118篇新版

普通话等级考试朗读范文含注音普通话考试朗读作品60篇 内含拼音与文字

2023年全国普通话等级考试(规则、练习材料、试题)全国通用大纲教材精华版+必考题整理+

普通话等级考试朗读范文含注音普通话考试朗读作品60篇 内含拼音与文字

国家普通话水平考试培训教程2022新版
 河南大学832生化真题总结
河南大学832生化真题总结
2023-07-07 40页
 暨南大学普通生物学名词解释
暨南大学普通生物学名词解释
2023-07-07 6页
 河南大学631普通生物学真题总结
河南大学631普通生物学真题总结
2023-07-07 11页
 2023年青海考研英语二真题(含答案)
2023年青海考研英语二真题(含答案)
2023-06-29 20页
 2023年青海考研数学三试题(含答案)
2023年青海考研数学三试题(含答案)
2023-06-29 16页
 2023年青海考研数学二试题(含答案)
2023年青海考研数学二试题(含答案)
2023-06-29 14页
 2023年湖北考研数学三试题(含答案)
2023年湖北考研数学三试题(含答案)
2023-06-29 16页
 2023年云南考研数学二试题(含答案)
2023年云南考研数学二试题(含答案)
2023-06-29 14页
 2023年甘肃考研数学三试题(含答案)
2023年甘肃考研数学三试题(含答案)
2023-06-29 16页
 2023年福建考研英语二真题(含答案)
2023年福建考研英语二真题(含答案)
2023-06-29 20页

